What is Proof of Stake? Simple Explanation
If you’re just getting into the blockchain world, you’ve probably heard a lot of terms you don’t understand. “Proof of stake”, Ethereum’s proof of stake, “mining,” and “consensus algorithms” are just a few examples. In this guide, we’ll break down what proof of stake is and how it works.
Consensus mechanism?
Before we go any further, it’s important to understand what consensus mechanism is and how it works. Consensus is the mechanism which all users of the network agree on the validity of transactions. Consensus algorithm validates every transaction in the network. Once a transaction is verified, it is then added to the blockchain where it cannot be changed or reversed.
There are three main types of consensus mechanisms / algorithms but the most well-known are:
- Proof of work
- Proof of stake
- Delegated proof of stake
In this article we will discuss about proof of stake model.
Proof of stake Definition
Proof of stake PoS is a consensus mechanism that allows users to validate transactions on the blockchain. PoS was first introduced by Scott Nadal and Sunny King in 2012. It was introduced to solve issues of proof of work consensus algorithm such as high energy consumption and scalability issues.
In contrast to proof of work, which requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions, proof of stake allows users to simply stake their coins in order to participate in the process. The aim of PoS is to create a more efficient, secured and sustainable consensus algorithm.
How does proof of stake work?
As we mentioned before, the aim of PoS is to create a more efficient, secured and sustainable way of validating transaction in the blockchain. To make it easy to understand, we have divided the explanation into three categories: Transactions, Block validation and Rewards.
Transactions
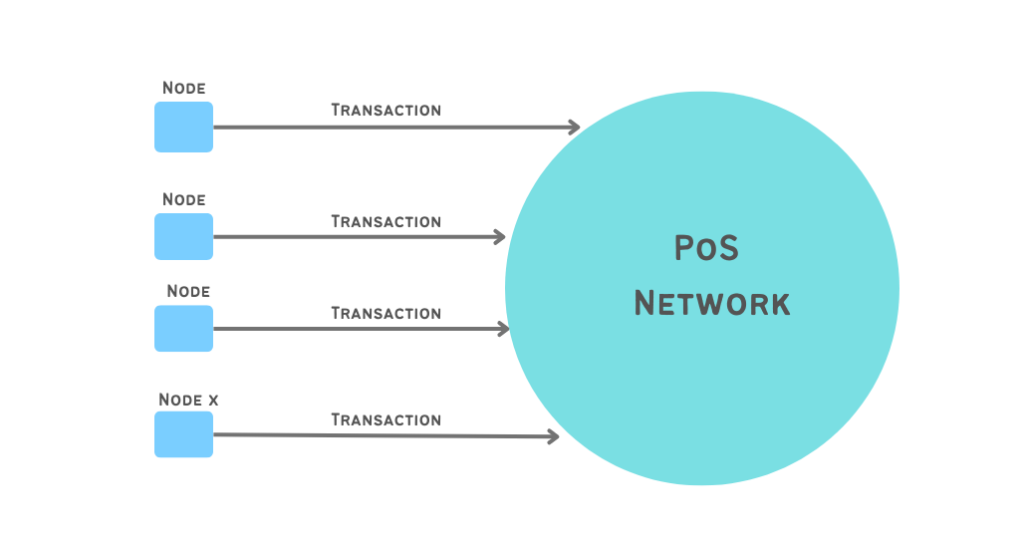
In blockchain a transaction is any activity that needs to be verified within the network, such as when coins are being sent or received. In proof of stake, nodes carry out transactions which are then gathered together in the PoS mechanism. All the nodes of the network have copies of the blockchain and when new transaction come in, they will be broadcasted to all the nodes in the network.
Block validation
Once the mechanism reaches the limit of transactions that a block can log, a validator must be chosen from the mechanism in order to validate the transactions of the new block and add it permanently to the blockchain.
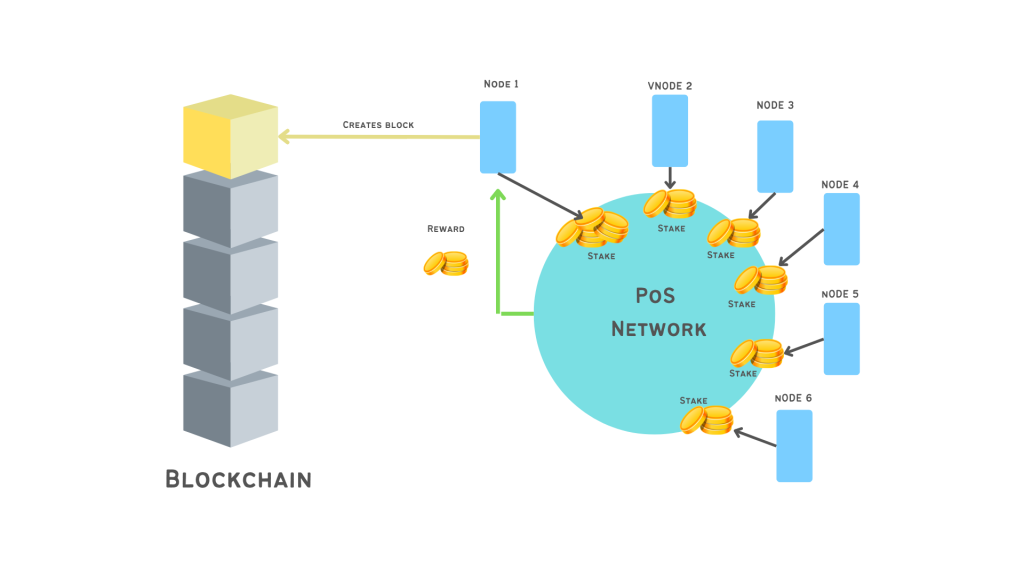
The Consensus algorithm of the PoS network randomly chooses the validators for each block. In order to be the next block writer, a node which will become a validator must first stake a certain number of coins as show on the image. It is important to note that in a proof of stake network all the nodes can become validators, however not all the nodes will have the same probability of being chosen as a validator.
The selection process of the validator for each block is completely random, but some nodes might have more chances than others to be chosen. There are different factors that the mechanism considers choosing the validator, such as the number of coins being staked and the length of time that they have been staked for.
Let’s say that the node 1 was chosen by the mechanism as the validator to verify the new block. Node 1 validates the transactions in block, while other nodes must verify that validation accuracy by performing their own validation.
Rewards
When Node 1 and the rest of the nodes complete successfully the validation and agree their records are valid, then the Node 1 will receive the reward by the mechanism. However, if the Node 1 verifies a fraudulent transaction on the block and the other validators do not validate that transaction, then coins of the Node 1 will be slashed (taken away) and the node might be removed from the network by the mechanism.
The amount of reward that the validator receives depends on several factors such as:
- Totally coins staked
- The age of the coins
- The size of the transaction
- The number of blocks that the validator has validated
There are different types of rewards that a validator can receive:
- Block reward: this is a fixed amount that is given to the validator for each block that he validates.
- Fees: these are the transaction fees that all the users in the network have to pay when they make a transaction.
The Benefits of Proof of Stake
There are several benefits that proof of stake has over proof of work.
1. Security
PoS is a much more secure algorithm than PoW. This is because in proof of work, the block creator is chosen based on their processing power, which can be bought with enough money. This makes proof of work vulnerable to 51 percent attacks, where someone with enough money can control the network. In proof of stake, the block creator is chosen based on their number of coins. So it would be much more expensive to mount a 51 percent attack.
2. Energy efficiency
Proof of stake is also a lot more energy efficient than proof of work. This is because in proof of work, miners need to use a lot of computational power. In proof of stake, the creator of the next block is chosen based on their number of coins, so they don’t need to use as much computational power.
3. Faster transactions
A key advantage of proof of stake is that transactions occur much faster. This uptick in speed is due to the fact that, with proof of work, miners must expend large amounts of energy trying to solve a complex mathematical problem as a way to earn the right to create the next block. In contrast, under proof of stake, the individual who gets to generate the subsequent block is picked based on their number staked coins.
4. Spend less money on hardware
An advantage that proof-of-stake is that you don’t need to spend large amounts of money on hardware. In proof of work, the individual miner needs a powerful computer to try and solve cryptographic puzzles quickly in order to have the chance create the next block. However, for Proof of Stake, this isn’t necessary because all you need are your coins!
Which coins uses proof-of-stake?
There are several cryptocurrencies that use proof of stake. Some of the most popular include:
- Ethereum
- NEO
- Cardano
- Solana
- Polkadot
How Can You Make Money with Proof of Stake?
There are several ways that you can make money with proof of stake.
1. Stake tokens
One of the simplest ways to make money with PoS is to simply stake your coins/token and earn rewards to verify transactions.
2. Delegating your staking
If you don’t have the time or resources to stake your own coins, you can always delegate your staking to someone else.
3. Participate in a staking pool
Another way to make money with proof of stake is to participate in a staking pool. Staking pools are groups of people who pool their resources together in order to increase their chances of earning rewards.
4. Run a master node
If you have a large number of coins, you can also run your own validator node, a Master node. Master nodes are special nodes that perform additional functions on the network, such as processing and verifying transactions and maintaining a copy of the blockchain.
5. Create a staking wallet
Another way to make money with proof of stake is to create a staking wallet. Staking wallets are wallets that allow users to earn rewards for holding their coins in the wallet.
Proof of stake security
PoS blockchains are more secure than proof of work blockchains. The reason is that a 51% attack is much harder to pull off on a PoS blockchain. In order for an attacker to verify blocks and control more than half of the coins that are staked, they would need to buy up a large amount of the currency, which would drive up the price and make it too expensive for them to continue buying.
Additionally, if an attacker did manage to control more than half of the coins that are staked, they would still need to have the support of the majority of users in order to make any changes to the network.
Proof of work vs proof of stake
Proof of work is the original consensus mechanism that was used by Bitcoin. It is a process where miners use their computing power to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions and verify new blocks to the blockchain.
Proof of stake, on the other hand, is a newer consensus mechanism that does not require miners to solve complex mathematical problems. Instead, anyone with a computer can participate in the process and earn rewards for validating transactions.
So, which one is better?
In terms of energy efficiency and scalability, proof of stake is superior to proof of work. In addition, because a 51 percent attack is much more difficult to execute, proof of stake is also more secure than proof of work. Overall, proof of stake is a more efficient and secure consensus mechanism than proof of work. However, there are people who would say proof of work is more secure because it’s the original consensus method that has been combat-tested over time.