What is Internet of Things (IoT) and How Does it Work – Beginner’s Guide
The Internet of Things has become one of the most popular subjects in the tech industry today, and the IoT ecosystem is expanding at a rapid pace. But what exactly is the internet of things? And how does it work? In this beginner’s guide, we’ll answer these questions and more.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT) technology
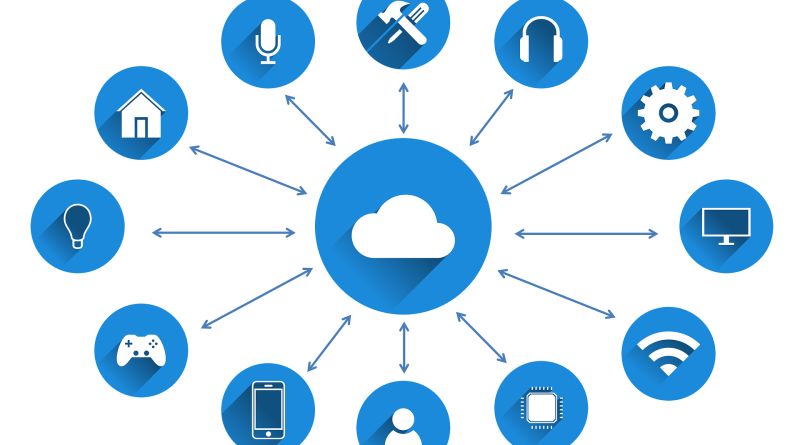
Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the interconnectedness of physical objects and devices, often referred to as smart devices or connected devices. Each connected device is equipped with sensors and other technology that allow them to collect data about the other IoT devices and themselves, as well as to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
IoT devices are connected to the internet via a variety of methods, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular data, and satellite. This allows data collected by IoT devices to be transmitted and processed by computers, which can then be used to provide insights or take actions based on the data.
The IoT allows objects to be sensed and/or controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, and resulting in improved efficiency, accuracy and economic benefit in addition to reduced human intervention.
In 2014 the Global Standards Initiative on Internet of Things (IoT-GSI) defined the IoT as “the infrastructure of the information society.” By this they meant a global infrastructure consisting of sensors and actuators embedded in physical objects (“things”), connected by networks, able to communicate and exchange data.
This definition is similar to the one used by the European Commission’s IoT Strategy Group, which in 2013 defined the IoT as “a global network infrastructure, based on existing and evolving interoperable information and communication technologies, where physical and virtual ‘things’ have identities, physical attributes, and virtual personalities and use intelligent interfaces, and are seamlessly integrated into the information network.”
How does the Internet of Things work?
The internet of things works by connecting devices to the internet and to each other. This connection allows devices to share data and information, which can be used to carry out a task or provide a service.
The key characteristic of the IoT is that it enables objects to be connected and controlled remotely across the internet making them smart objects. This means that devices that were previously isolated from the internet can now be connected to it, allowing them to communicate with each other and exchange data.
The IoT is made up of three main components:
- Things: Physical objects that are connected to the internet and can collect and exchange data.
- Connectivity: A network that allows things to connect to each other and share data.
- Analytics and applications: Software that analyses IoT data and provides information or controls them.
The steps IoT works:
- The first step in making the IoT work is to connect devices to the internet. This can be done using a variety of technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee or cellular data.
- Once devices are connected to the internet, they can be connected to each other. This allows them to share data and information, which can be used to carry out a task or provide a service.
- The third step is to use analytics and applications to analyse the data from devices and provide information or controls using different machine learning algorithms. This step is important in order to make the IoT work effectively and efficiently. Applications and analytics can be used to control devices, such as turning on a light when a person enters a room, or to provide information, such as an alert when a device is low on battery.
Examples of Internet of Things applications
There are many potential applications for the internet of things. Some examples include:
- Home automation: Connecting devices in the home, such as lights, appliances and security systems, to the internet so they can be controlled remotely.
- Wearables: Connecting wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, to the internet so they can collect and exchange data.
- Connected cars: Connecting cars to the internet so they can share data with each other and with road infrastructure, such as traffic lights and parking spaces.
- Smart cities: Connecting devices in cities, such as streetlights and rubbish bins, to the internet so they can be managed and controlled remotely.
- Industrial internet of things: Connecting industrial devices, such as machines and IoT sensors, to the internet so they can be monitored and controlled remotely.
The internet of things has the potential to transform the way we live, work and interact with the world. It has the potential to make our lives easier and more efficient, and to create new and innovative services and applications.
Examples of IoT devices – smart devices
There are many different types of smart devices that can be used in the internet of things. Some examples include:
- Smart thermostats: Adjust heating and cooling in a home or office based on occupancy and temperature.
- Smart lights: Turn on/off and dim lights remotely, and change light colours.
- Smart security IoT system: Monitor and control security systems remotely.
- Smart door locks: Lock and unlock doors remotely.
- Smart appliances: Control appliances remotely, such as washing machines and dryers.
Examples of IoT sensors
There are many different types of IoT sensors that can be used to collect data. Some examples include:
- Temperature sensors: Measure temperature and report changes.
- Humidity sensors: Measure humidity and report changes.
- Pressure sensors: Measure pressure and report changes.
- Light sensors: Measure light levels and report changes.
- Motion sensors: Detect movement and report changes.
- Sound sensors: Measure noise levels and report changes.
IoT devices and sensors can be used to collect a wide variety of data. This data can be used to provide information or control devices. For example, a temperature sensor data can be used to turn on a fan when the temperature gets too hot, or data from a motion sensor can be used to turn on a light when someone enters a room. IoT data can also be used to provide information about the environment, such as air quality or traffic conditions. This data can be used to improve the efficiency of services, such as public transport or waste management.
IoT device management
One of the challenges of the IoT is managing the huge number of devices that are connected to the internet. This is because each device needs to be given a unique identifier (ID), which can be used to track and manage it.
Device management is a crucial part of making the IoT work, and there are a variety of ways to do it. One common method is to use an IoT platform, which is a software that helps to manage devices and their data.
IoT platforms typically provide a way to connect devices to the internet, a way to store and analyse data, and a way to control devices. They can also provide other features, such as push notifications, security and authentication.
An example of an IoT platform is IBM Watson IoT, which is a cloud-based platform that helps to manage and analyse data from devices.
IoT security
One of the challenges of the IoT is security. This is because the IoT involves a large number of consumer IoT devices that are connected to the internet and share data. This means that there is a greater risk of data being leaked or hacked considering the number of data breaches have happened. Check more for cloud storage security.
To secure the IoT, it is important to consider security at all stages, from the design of devices to the way they are managed and monitored.
At the device level, security can be implemented by using encryption, which makes it difficult for data to be intercepted and read. Other measures, such as password protection through password manager and two-factor authentication, can also be used to protect data.
At the network level, security can be implemented by using firewalls and intrusion detection systems. These systems can help to prevent data being intercepted or hacked.
At the platform level, IoT systems security can be implemented by using access control measures, such as authentication and authorization. This can help to ensure that only authorized users can access data.
Conclusion
The internet of things has the potential to transform the way we live, work and interact with the world. It has the potential to make our lives easier and more efficient, and to create new and innovative services and applications. However, there are still some challenges that need to be overcome in order for the IoT to reach its full potential. With the right solutions, the IoT can become a reality and make our lives better.